Two-wire Cable between Electrical Wiring and Appliance
Task number: 1537
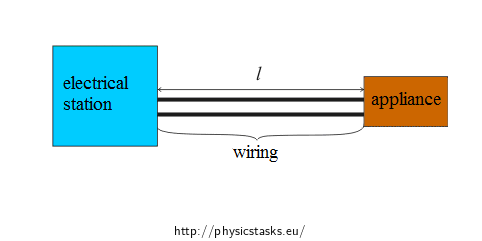
Output voltage of electrical wiring is 5.6 kV. An appliance is at a distance 10 km from a station. Determine the cross-section of a copper wire which is used for two-wire cable between the wiring and the appliance, provided that the current is 20 A and the voltage losses in the conductors should not exceed 3%.
Hint 1
How to calculate a surface area of a cross section? Note that the wire is a conductor with a constant cross section.
Hint 2: Losses of two-wire cable
For a better idea, draw a two-wire cable as a circuit with the appliance.
What does it mean that the losses must not exceed 3 %? What physical quantity represents the losses? Think about how this quantity behaves in the circuit above.
Solution
To determine the cross section S of the wire, we use the relation for calculation of resistance of a wire with a constant cross section \[R=\frac{\rho l}{S} \qquad \Rightarrow \qquad S={\rho l}{R},\] where R is the resistance of the conductor, ρ is the electrical resistivity of the conductor material, which can be found in The Handbook of Chemistry and Physics and l is the length of the conductor.
We use Ohm's law to determine the resistance R \[R=\frac{U}{I},\] where U is the voltage and I is the current in the conductor.
What is a two-wire cable? For a better idea we draw the two-wire cable as a circuit with the appliance.We evaluate the losses through the electric power P. In electric circuit the following applies \[P=U I,\] where U is voltage and I is the current in the circuit. The current in the circuit is constant. Therefore, the power losses are represented by the voltage losses. The voltage is divided into the two wires and the appliance. The losses on the wiring can be maximum 3 % of the total voltage. That is 1.5 % on each wire. The voltage on the conductor Uc is expressed as: \[U_V=0{,}015\,U.\]
Now we put the above together and we obtain the final relation for the cross section S of the wire \[ S = \frac{l\rho}{R}=\frac{l\rho}{\frac{U_V}{I}}=\frac{Il\rho}{0.015\,U}. \]
Given values and numerical substitution
U = 5.6 kV = 5 600 V Output voltage of the electrical wiring l = 10 km = 10 000 m Distance between the appliance and the station I = 20 A Electric current in the wiring UV = 0.015U V Voltage on one conductor S = ? m2 Cross section of the conductor From The Handbook of Chemistry and Physics: ρ = 0.018 μΩm Electrical resistivity of copper
\[S=\frac{I\rho l}{0.015\,U}=\frac{20{\cdot} 0.018{\cdot} 10^{-6}\cdot 10\,000}{0.015{\cdot} 5\,600}\,\dot{=}\,43 {\cdot} 10^{-6}\, \mathrm {m^2}=43\, \mathrm {mm^2}\]Answer
The cross section of a wire must be 43 mm2 at minimum.