“Divided” RLC circuit
Task number: 662
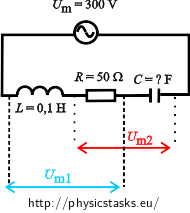
A capacitor with an unknown capacity, a resistor with resistance 50 Omega; and a coil with inductance 0.10 H are connected in series in sn alternating circuit with frequency 50 Hz and amplitude of voltage 300 V. The ratio of amplitudes of the voltage in two parts of the circuit which are marked in the picture is Um1:Um2 = 1:2. Calculate the capacity of the capacitor and the amplitude of the current in the circuit.
Notation
From the assignment we know:
Frequency of the circuit f = 50 Hz Voltage of the power supply Um = 300 V Resistance of the resistor in the circuit R = 50 Ω Inductance of the coil in the circuit L = 0.10 H Ratio of voltages marked in the picture Um1:Um2 = 1:2 We should find out:
Capacity of the unknown capacitor C = ? (F) Amplitude of a current in the circuit Im = ? (A) Hint 1
For the RLC circuit connected in series is true that the current which flows through each of the components of the circuit is the same.
Hint 2
We can imagine the parts of the circuit with marked voltages as two separate circuits with a given total voltage. Currents which flow through these circuits are the same because it is a RLC circuit in series in fact.
Analysis
We have chosen two parts in the circuit in the picture from assigned task. We „know“ the amplitude of the voltage of each of them so we can solve each part as a separate circuit. We use Ohm’s law for an alternating circuit. The current is the same in both of the circuits, so we can formulate the capacity from the ratio of voltages.
We gain the amplitude of current from Ohm’s law which we use for the whole circuit.
Expressing of a voltage Um1 and Um2
A coil with an inductance L and a resistor with resistance R are connected to the part of the circuit which belonges to voltage Um1. The coil and the resistor are connected in series.
We formulate impedance Z1 of this part of the circuit:
\[ Z_1= \sqrt{R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2}=\sqrt{R^2+X_L^2}.\]And substitute it to Ohm’s law:
\[U_{m1}=I_m Z_1=I_m\sqrt{R^2+X_L^2}=I_m \sqrt{R^2+(\omega L)^2}. \]Formulas for the second part of the circuit, to which belongs voltage Um2 are similar. In this circuit we have a resistor with resistivity R and a capacitor with an unknown capacity C:
\[Z_2= \sqrt{R^2+(X_L-X_C)^2}=\sqrt{R^2+X_C^2}\] \[U_{m2}=I_m Z_2=I_m\sqrt{R^2+X_C^2}=I_m \sqrt{R^2+\frac{1}{(\omega C)^2}}. \]Numerical solution
Capacity of the capacitor:
\[C=\frac{1}{\omega \sqrt{3R^2+4(\omega L)^2}}=\frac{1}{2 \cdot \pi \cdot 50 \sqrt{3{\cdot} 50^2+4(2\cdot \pi\cdot 50{\cdot} 0.1)^2}}\,\mathrm{F}\] \[ C \dot= 30 {\cdot} 10^{-6} \,\mathrm{F}=30\,\mathrm{\mu F}\]Amplitude of the current:
\[I_m=\frac{U_m}{Z}=\frac{U_m}{\sqrt{R^2+(\omega L-\frac{1}{\omega C})^2}}\] \[I_m=\frac{300}{\sqrt{50^2+(2\cdot\pi\cdot 50 {\cdot} 0.1 - \frac{1}{2\cdot \pi \cdot 50 {\cdot} 30\cdot 10^{-6}})^2}}\,\mathrm{A} \] \[I_m \dot= 3.3 \,\mathrm{A} \]Answer
Capacity of the capacitor connected in series is approximately: C = 30 μF.
Amplitude of the alternating current in the circuit is approximately: Im = 3.3 A.