Capacitors
Task number: 298
Three capacitors (with capacitances C1, C2 and C3) and power supply (U) are connected in the circuit as shown in the diagram.
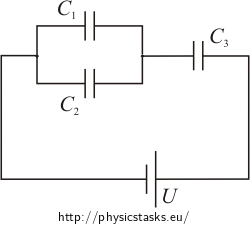
a) Find the total capacitance of the capacitors’ part of circuit and total charge Q on the capacitors.
b) Find the voltage and charge on each of the capacitors.
Hint: Capacitance
When capacitors are connected in parallel the total capacitance is equal to the sum of the single capacitances.
\[C\,=\,C_1+C_2+C_3\]When connected in series the reciprocal value of total capacitance is equal to the sum of reciprocal values of the single capacitances.
\[\frac{1}{C}\,=\,\frac{1}{C_1}+\frac{1}{C_2}+\frac{1}{C_3}\]Hint: Voltage and charge
When the capacitors are connected in series there is the same charge on each of them. The total voltage is sum of the single voltages.
\[Q\,=\,Q_1\,=\,Q_2\,=\,Q_3\] \[U\,=\,U_1+U_2+U_3\]When the capacitors are connected in parallel the total charge is the sum of the single charges. There is the same voltage on each of them.
\[Q\,=\,Q_1+Q_2+Q_3\] \[U\,=\,U_1\,=\,U_2\,=\,U_3\]Analysis
Capacitors connected in parallel can be effectively substituted by one capacitor with capacitance equal to the sum of substituted capacitors’ capacitances. By this step we can get a simpler circuit with 2 capacitors connected in series. When capacitors connected in series, we can replace them by one capacitor with capacitance equal to reciprocal value of sum of reciprocal values of several capacitors’ capacitances. So we can evaluate the total capacitance.
Total charge is directly proportional to the total capacitance and also to the total voltage (i.e. power supply voltage).
Charges on capacitors in series are equal to each other and in this case also equal to the total charge. Therefore the charge on the third capacitor is equal to the total charge. If we know the charge, we can evaluate the voltage on the third capacitor.
Voltages on both capacitors connected in parallel are the same. We can evaluate them as the difference between the total voltage and voltage on the third capacitor. If we know the voltage and capacitance, we can evaluate the charge on each of these two capacitors.
Solution: Total capacitance and total charge
Capacitors C1 and C2 connected in parallel can be substituted with one capacitor C12 with capacitance equal to the sum of several capacitances: C12 = C1+C2.
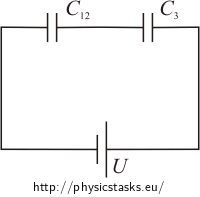
After this substitution there are 2 capacitors in the circuit - C12 and C3 connected in series.
\[\frac{1}{C}\,=\,\frac{1}{C_{12}}+\frac{1}{C_3}\, \Rightarrow\,C\,=\,\frac{C_{12}C_3}{C_{12}+C_3}=\,\frac{(C_1+C_2)C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\]Total charge Q can be evaluated using Q = UC \[Q=UC=\,\frac{U(C_1+C_2)C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\tag{1}\]
Solution: Charges and voltages on several capacitors
The charge and the voltage on the third capacitor:
The charges on capacitors C12 and C3 are equal and are equal to the total charge Q.
\[Q\,=\,Q_{12}\,=\,Q_3\]So the voltage on the third capacitor is:
\[U_3\,=\,\frac{Q_3}{C_3}\,=\,\frac{Q}{C_3}\]We have already evaluated the charge Q in the previous section, so we can replace them in the equation:
\[U_3\,=\,\frac{U \left( C_1+C_2 \right)C_3}{ \left( C_1+C_2+C_3\right)C_3}\,= \,\frac{U \left( C_1+C_2 \right)}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\tag{*}\]
Voltages on capacitors connected inparallel:
The total voltage U is divided between capacitors C12 and C3.
\[U\,=\,U_{12}+U_3\]Using that we can evaluate the voltage U12
\[U_{12}\,=\,U-U_3\]We can replace the voltage U3 with (*).
\[U_{12}\,=\,U-\frac{U \left( C_1+C_2 \right)}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\]Let’s convert it to a common denominator and simplify by combining like terms.
\[U_{12}\,=\,\frac{U \left( C_1+C_2+C_3 \right)-U \left( C_1+C_2 \right)}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\,=\,\frac{UC_3}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\tag{**}\]Voltages on capacitors C1 and C2 connected in parallel are the same:
\[U_1\,=\,U_2\,=\,U_{12}\]
Charges on capacitors connected in parallel:
Using the voltage on each capacitor from (**) we can simply evaluate charges on capacitors connected in parallel:
\[Q_1=U_1C_1\] \[Q_2=U_2C_2\] \[Q_1=\,\frac{UC_1C_3}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\] \[Q_2=\,\frac{UC_2C_3}{ C_1+C_2+C_3}\]Final formulas
Total capacitance and total charge of the circuit:
\[C\,=\,\frac{(C_1+C_2)C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\] \[Q\,=\,\frac{U(C_1+C_2)C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\]Charges on several capacitors:
\[Q_1\,=\,\frac{UC_1C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\] \[Q_2\,=\,\frac{UC_2C_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\] \[Q_3\,=\,Q\]Voltages on several capacitors:
\[U_1\,=\,U_2\,=\,\frac{UC_3}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\] \[U_3\,=\,\frac{U\left(C_1+C_2\right)}{C_1+C_2+C_3}\]